
Our technology inevitably comes with us when we travel. Some people won’t even travel to the end of the block without their smartphones. Whether you travel for work or pleasure, not having your technology there when you need it can ruin your day.
Travel smarter and more securely by doing several checks before you go. Use our handy tech travel checklist below, it can save you from lost devices or a data breach.
1. Check Your Apps
Have you ever sat at an airport gate wondering why it looked so empty? You then found out that your gate had changed, and you had no idea. You go rushing to the other end of the concourse, hoping you’re not too late.
How did everyone else know about the gate change? They most likely had the app for the airline and received a notification.
Before you leave for a trip, make sure to download any apps you may need. It’s better to download them when you’re at home on your own Wi-Fi. Waiting until you’re at the airport could cause connectivity or security issues.
Some of the apps you may want to download or update before your trip are:
- Airline app
- Train app
- Hotel app
- Weather app
- City tourism app
2. Check Your Cords & Adapters
People leave behind countless chargers and adapters every day. They litter airports, restaurants, and train stations around the world. Make sure to bring a backup charger for your laptop, tablet, or phone. Otherwise, you may find yourself paying a premium price for a new charger in a gift shop.
3. Check Your Power
A great way to ensure you have the power you need is to buy a small portable battery. You can find these in most major retailers or online. They are small “blocks” that hold a charge and can power up a cell phone in a pinch.
Having this extra backup also helps you avoid potential juice-jacking ports. These are fake or compromised public USB charging ports that hackers use them to steal your data when you plug in your device.
4. Check Your Mobile Plan
Traveling for work is exciting, but it can also lead to issues connecting with clients. Being away from the office means missed calls an unheard voicemails.
Handing out you personal mobile number may seem like a good solution. However, having clients or coworkers reach you at all hours of the day can blur the line between your professional and personal life. It can also get expensive if you’re on long calls or using your own mobile data.
An alternative is to set up a VoIP app that you can use with your office while you’re traveling. These enable both calls and SMS, but you do need an internet connection.
Interested in learning more about VoIP and the functions it provides? Reach out to Databranch today! Our Rock-It VoIP platform offers flexibility and scalability to accommodate for fluctuations and growth in your business, and we can service locations nationwide. With Rock-IT VoIP, we also port your numbers so they stay the same and handle any upgrades, maintenance, and programming!
5. Check or Add a VPN
Free Wi-Fi may be a welcome site when you’re on the road, but it can also be dangerous. You don’t know who else is using that Wi-Fi. A hacker hanging out on the connection can easily steal your data if you’re not protected.
It’s better to use either your mobile carrier connection or a virtual private network (VPN) app. VPN plans are inexpensive and will keep your data encrypted, even if you’re on public Wi-Fi.
Visit our website here to learn more about VPNs and what factors to consider when choosing a plan.
6. Check Your Backup
Unfortunately, mishaps occur when traveling. You may leave your phone behind in the airport, have your luggage lost, or get your device stolen while in a crowded area.
10% of all laptop thefts happen in airports.
Don’t lose all your work data with the device! Back up your devices to the cloud or local storage before you travel. This ensures that you won’t lose the valuable information on your device.
Need help with a Data Backup and Recovery plan for your business? Contact us today or visit our website to learn more.
7. Check Your Device Security
Make your devices as secure as possible before you hit the road. When we’re traveling, our minds are occupied by other things. So, you may not think to check your antivirus or avoid suspicious phishing links.
Protect your devices before you go using:
- Antivirus/anti-malware
- DNS filtering
- Screen lock with passcode
- Sharing features turned off
- VPN application
- Find-My-Device feature turned on
Improve the Security of Your Devices Now
Don’t leave your company devices unprotected. Contact us today if you want to discuss your cybersecurity in greater detail. We can arrange a quick chat to discussed some options we have available that would help enhance your businesses security. Give us a call at 716-373-4467 x 115 or email us at [email protected] to learn more.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

Phishing. It seems you can’t read an article on cybersecurity without it coming up. That’s because phishing is still the number one delivery vehicle for cyberattacks.
A cybercriminal may want to steal employee login credentials, launch a ransomware attack, or possibly plant spyware to steal sensitive info. For a hacker, sending a phishing email can accomplish all of this.
80% of surveyed security professionals say that phishing campaigns have significantly increased post-pandemic.
Phishing not only continues to work, but it’s also increasing in volume due to the increase in remote workers. Many employees are now working from home and don’t have the same network protections they had when working at the office.
Why has phishing continued to work so well after all these years? Aren’t people finally learning what phishing looks like?
It’s true that people are generally more aware of phishing emails and have gotten better at stopping them. However, it’s also true that these emails are becoming harder to recognize as scammers evolve their tactics.
One of the newest tactics is particularly hard to detect, the reply-chain phishing attack.
What is a Reply-Chain Phishing Attack?
Just about everyone is familiar with reply chains in email. An email is sent to one or more people, one replies, and that reply sits at the bottom of the new message. Then another person chimes in on the conversation, replying to the same email.
Soon, you have a chain of email replies on a particular topic. It lists each reply one under the other so everyone can follow the conversation.
You don’t expect a phishing email tucked inside that ongoing email conversation. Most people are expecting phishing to come in as a new message, not a message included in an ongoing reply chain.
The reply-chain phishing attack is particularly insidious because it does exactly that. It inserts a convincing phishing email in the ongoing thread of an email reply chain.
How Does a Hacker Gain Access to the Reply Chain?
How does a hacker gain access to the reply chain conversation? By hacking the email account of one of those people copied on the email chain.
The hacker can email from an email address that the other recipients recognize and trust. They also gain the benefit of reading down through the chain of replies. This enables them to craft a response that looks like it fits.
For example, they may see that everyone has been weighing in on a new product idea. So, they send a reply that says, “I’ve drafted up some thoughts on the new product, here’s a link to see them.”
The link will go to a malicious phishing site. The site might infect a visitor’s system with malware or present a form to steal more login credentials.
The reply won’t seem like a phishing email at all. It will be convincing because:
- It comes from an email address of a colleague. This address has already been participating in the email conversation.
- It may sound natural and reference items in the discussion.
- It may use personalization. The email can call others by the names the hacker has seen in the reply chain.
Business Email Compromise is Increasing
Business email compromise (BEC) is so common that it now has its own acronym. Weak and unsecured passwords lead to email breaches. So do data breaches that reveal databases full of user logins. Both are contributors to how common BEC is becoming.
In 2021, 77% of organizations saw business email compromise attacks. This is up 65% compared to the year before.
Credential theft has become the main cause of data breaches globally.
The reply-chain phishing attack is one of the ways that hackers turn that BEC into money. They either use it to plant ransomware or other malware or to steal sensitive data to sell on the Dark Web.
Tips for Addressing Reply-Chain Phishing
Here are some ways that you can lessen the risk of reply-chain phishing in your organization:
- Use a Business Password Manager: This reduces the risk that employees will reuse passwords across many apps. It also keeps them from using weak passwords since they won’t need to remember them anymore. Click here to learn more about our password manager solution, LastPass.
- Put Multi-Factor Controls on Email Accounts: Present a system challenge (question or required code). Using this for email logins from a strange IP address can stop account compromise. You can learn more about MFA here.
- Teach Employees to be Aware: Awareness is a big part of catching anything that might be slightly “off” in an email reply. Many attackers do make mistakes. Our Security Awareness Training will give your employees the tools they need to identify threats. Click here to learn more.
How Strong Are Your Email Account Protections?
Do you have enough protection in place on your business email accounts to prevent a breach? Let us know if you’d like some help!
Databranch has a foundation security suite with systems in place to identify any anomalies before cyber criminals have a chance to do significant damage to your network. Contact us at 716-373-4467 x 15, [email protected], or request more information below.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

Stolen login credentials are a hot commodity on the Dark Web. There’s a price for every type of account from online banking to social media. For example, hacked social media accounts will go for between $30 to $80 each.
The rise in reliance on cloud services has caused a big increase in breached cloud accounts. Compromised login credentials are now the #1 cause of data breaches globally, according to IBM Security’s latest Cost of a Data Breach Report.
Having either a personal or business cloud account compromised can be very costly. It can lead to a ransomware infection, compliance breach, identity theft, and more.
To make matters more challenging, users are still adopting bad password habits that make it all too easy for criminals. For example:
- 34% of people admit to sharing passwords with colleagues
- 44% of people reuse passwords across work and personal accounts
- 49% of people store passwords in unprotected plain text documents
Cloud accounts are more at risk of a breach than ever, but there are several things you can do to reduce the chance of having your online accounts compromised.
Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is the best method there is to protect cloud accounts. While not a failsafe, it is proven to prevent approximately 99.9% of fraudulent sign-in attempts, according to a study cited by Microsoft.
When you add the second requirement to a login, which is generally to input a code that is sent to your phone, you significantly increase account security. In most cases, a hacker is not going to have access to your phone or another device that receives the MFA code, thus they won’t be able to get past this step.
The brief inconvenience of using that additional step when you log into your accounts is more than worth it for the bump in security.
Use a Password Manager for Secure Storage
One way that criminals get their hands on user passwords easily is when users store them in unsecured ways. Such as in an unprotected Word or Excel document or the contact application on their PC or phone.
Using a password manager provides you with a convenient place to store all your passwords that is also encrypted and secured. Plus, you only need to remember one strong master password to access all the others.
Password managers can also autofill all your passwords in many different types of browsers, making it a convenient way to access your passwords securely across devices.
Review/Adjust Privacy & Security Setting
Have you taken time to look at the security settings in your cloud tools? One of the common causes of cloud account breaches is misconfiguration. This is when security settings are not properly set to protect an account.
You don’t want to just leave SaaS security settings at defaults, as these may not be protective enough. Review and adjust cloud application security settings to ensure your account is properly safeguarded.
Use Leaked Password Alerts in Your Browser
You can have impeccable password security on your end, yet still have your passwords compromised. This can happen when a retailer or cloud service you use has their master database of usernames and passwords exposed and the data stolen.
When this happens, those leaked passwords can quickly end up for sale on the Dark Web without you even knowing it.
Due to this being such a prevalent problem, browsers like Chrome and Edge have had leaked password alert capabilities added. Any passwords that you save in the browser will be monitored, and if found to be leaked, you’ll see an alert when you use it.
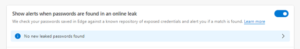
Look for this in the password area of your browser, as you may have to enable it. This can help you know as soon as possible about a leaked password, so you can change it.
Don’t Enter Passwords When on a Public Wi-Fi
Whenever you’re on public Wi-Fi, you should assume that your traffic is being monitored. Hackers like to hang out on public hot spots in airports, restaurants, coffee shops, and other places so they can gather sensitive data, such as login passwords.
You should never enter a password, credit card number, or other sensitive information when you are connected to public Wi-Fi. You should either switch off Wi-Fi and use your phone’s wireless carrier connection or use a virtual private network (VPN) app, which encrypts the connection.
Use Good Device Security
If an attacker manages to breach your device using malware, they can often breach your accounts without a password needed. Just think about how many apps on your devices you can open and already be logged in to.
To prevent an online account breach that happens through one of your devices, make sure you have strong device security. Best practices include:
- Antivirus/anti-malware
- Up-to-date software and OS
- Phishing protection (like email filtering and DNS filtering)
Looking for Password & Cloud Account Security Solutions?
Don’t leave your online accounts at risk. We can help you review your current cloud account security and provide helpful recommendations. Contact Databranch today at 716-373-4467 x 15 or [email protected] if you would like to enhance your security and want to discuss you options.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

The global damage of cybercrime has risen to an average of $11 million USD per minute, which is a cost of $190,000 each second.
60% of small and mid-sized companies that have a data breach end up closing their doors within six months because they can’t afford the costs. The costs of falling victim to a cyberattack can include loss of business, downtime/productivity losses, reparation costs for customers that have had data stolen, and more.
You may think that this means investing more in cybersecurity, and it is true that you need to have appropriate IT security safeguards in place (anti-malware, firewall, etc.). However, many of the most damaging breaches are due to common cybersecurity mistakes that companies and their employees make.
The 2021 Sophos Threat Report, which looked at thousands of global data breaches, found that what it termed “everyday threats” were some of the most dangerous. The report stated, “A lack of attention to one or more aspects of basic security hygiene has been found to be at the root cause of many of the most damaging attacks we’ve investigated.”
Is your company making a dangerous cybersecurity mistake that is leaving you at high risk for a data breach, cloud account takeover, or ransomware infection?
Here are several of the most common missteps when it comes to basic IT security best practices.
NOT IMPLEMENTING MUTI-FACTOR AUTHENTICATION (MFA)
Credential theft has become the top cause of data breaches around the world, according to IBM Security. With most company processes and data now being cloud-based, login credentials hold the key to multiple types of attacks on company networks.
Not protecting your user logins with multi-factor authentication is a common mistake and one that leaves companies at a much higher risk of falling victim to a breach.
MFA reduces fraudulent sign-in attempts by a staggering 99.9%.
IGNORING THE USE OF SHADOW IT
Shadow IT is the use of cloud applications by employees for business data that haven’t been approved and may not even be known about by a company.
Shadow IT use leaves companies at risk for several reasons:
- Data may be used in a non-secure application
- Data isn’t included in company backup strategies
- If the employee leaves, the data could be lost
- The app being used might not meet company compliance requirements
Employees often begin using apps on their own because they’re trying to fill a gap in their workflow and are unaware of the risks involved with using an app that hasn’t been vetted by their company’s IT team.
It’s important to have cloud use policies in place that spell out for employees the applications that can and cannot be used for work.
THINKING YOU’RE FINE WITH ONLY AN ANTIVIRUS APPLICATION
No matter how small your business is, a simple antivirus application is not enough to keep you protected. In fact, many of today’s threats don’t use a malicious file at all.
Phishing emails will contain commands sent to legitimate PC systems that aren’t flagged as a virus or malware. Phishing also overwhelmingly uses links these days rather than file attachments to send users to malicious sites. Those links won’t get caught by simple antivirus solutions.
You need to have a multi-layered strategy in place that includes things like:
- Next-gen anti-malware (uses AI and machine learning)
- Next-gen firewall
- Email filtering
- DNS filtering
- Automated application and cloud security policies
- Cloud access monitoring
Databranch provides these foundational elements to all their managed service clients to ensure the protection of their business. Reach out at 716-373-4467 x 15 or [email protected] if you would like to learn more about our Foundation Security Platform and how we can help your organization be more secure.
NOT HAVING DEVICE MANAGEMENT IN PLACE
A majority of companies around the world have had employees working remotely from home since the pandemic, and they’re planning to keep it that way. However, device management for those remote employee devices as well as smartphones used for business hasn’t always been put in place.
If you’re not managing security or data access for all the endpoints (company and employee-owned) in your business, you’re at a higher risk of a data breach.
If you don’t have one already, it’s time to put a device management application in place, like Intune in Microsoft 365 or IBM’s MaaS 360 platform.
NOT PROVIDING ADEQUATE TRAINING TO EMPLOYEES
An astonishing 95% of cybersecurity breaches are caused by human error. Too many companies don’t take the time to continually train their employees, and thus users haven’t developed the skills needed for a culture of good cybersecurity.
Employee IT security awareness training should be done throughout the year, not just annually or during an onboarding process. The more you keep IT security front and center, the better equipped your team will be to identify phishing attacks and follow proper data handling procedures.
Some ways to infuse cybersecurity training into your company culture include:
- Short training videos
- IT security posters
- Webinars
- Team training sessions
- Cybersecurity tips in company newsletters
Click here to learn more about our continuous security awareness training program.
WHEN DID YOU LAST HAVE A CYBERSECURITY CHECKUP?
Don’t stay in the dark about your IT security vulnerabilities. Contact us today if you want to discuss your cybersecurity in greater detail and pinpoint potential risks. We can arrange a quick chat to review our Foundation Security Platform and how it can help enhance your organization’s security posture. Give us a call at 716-373-4467 x 15 or email us at: [email protected] to learn more.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More

In 2020, 75% of companies around the world experienced a phishing attack. Phishing remains one of the biggest dangers to your business’s health and wellbeing because it’s the main delivery method for all types of cyberattacks.
One phishing email can be responsible for a company succumbing to ransomware and having to face costly downtime. As many as 92% of data breaches are due to human error such as falling for a phishing email. This can result in a user unknowingly handing over the credentials to a company email account that the hacker then uses to send targeted attacks to customers.
Phishing takes advantage of human error, and some phishing emails use sophisticated tactics to fool the recipient into divulging information or infecting a network with malware.
Mobile phishing threats skyrocketed by 161% in 2021.
Your best safeguards against the continuous onslaught of phishing include:
- Email filtering
- DNS filtering
- Next-gen antivirus/anti-malware
- Ongoing employee cybersecurity awareness training
To properly train your employees and ensure your IT security is being upgraded to meet the newest threats you need to know what new phishing dangers are headed your way.
Here are some of the latest phishing trends that you need to watch out for in 2022.
PHISHING IS INCREASINGLY BEING SENT VIA TEXT MESSAGE
Fewer people are suspicious of text messages than they are of unexpected email messages. Most phishing training is usually focused on the email form of phishing because it’s always been the most prevalent.
But cybercrime entities are now taking advantage of the easy availability of mobile phone numbers and using text messaging to deploy phishing attacks. This type of phishing (called “smishing”) is growing in volume.
People are receiving more text messages now than they did in the past, due in large part to retailers and service businesses pushing their text updates for sales and delivery notices.
This makes it even easier for phishing via SMS to fake being a shipment notice and get a user to click on a shortened URL.
BUSINESS EMAIL COMPROMISE IS ON THE RISE
Ransomware has been a growing threat over the last few years largely because it’s been a big money-maker for the criminal groups that launch cyberattacks. A new up-and-coming form of attack is beginning to be quite lucrative and thus is also growing.
Business email compromise (BEC) is on the rise and being exploited by attackers to make money off things like gift card scams and fake wire transfer requests.
What makes BEC so dangerous (and lucrative) is that when a criminal gains access to a business email account, they can send very convincing phishing messages to employees, customers, and vendors of that company. The recipients will immediately trust the familiar email address, making these emails potent weapons for cybercriminals.
Enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is one of the best ways you can protect yourself and your business from BEC. Reach out to Databranch with any questions or if you would like assistance setting up MFA for your companies users.
SMALL BUSINESSES ARE BEING TARGETED MORE FREQUENTLY WITH SPEAR PHISHING
There is no such thing as being too small to be attacked by a hacker. Small businesses are targeted frequently in cyberattacks because they tend to have less IT security than larger companies.
43% of all data breaches target small and mid-sized companies, and 40% of small businesses that become victims of an attack experience at least eight hours of downtime as a result.
Spear phishing is a more dangerous form of phishing because it’s targeted and not generic. It’s the type deployed in an attack using BEC.
It used to be that spear-phishing was used for larger companies because it takes more time to set up a targeted and tailored attack. However, as large criminal groups and state-sponsored hackers make their attacks more efficient, they’re able to more easily target anyone.
A result is small businesses receiving more tailored phishing attacks that are harder for their users to identify as a scam.
THE USE OF INITIAL ACCESS BROKERS TO MAKE ATTACKS MORE EFFECTIVE
We just discussed the fact that large criminal groups are continually optimizing their attacks to make them more effective. They treat cyberattacks like a business and work to make them more profitable all the time.
One way they are doing this is by using outside specialists called Initial Access Brokers. This is a specific type of hacker that only focuses on getting the initial breach into a network or company account.
The increasing use of these experts in their field makes phishing attacks even more dangerous and difficult for users to detect.
BUSINESS IMPERSONATION IS BEING USED MORE OFTEN
As users have gotten savvier about being careful of emails from unknown senders, phishing attackers have increasingly used business impersonation. This is where a phishing email will come in looking like a legitimate email from a company that the user may know or even do business with.
Amazon is a common target of business impersonation, but it also happens with smaller companies as well. For example, there have been instances where website hosting companies have had client lists breached and those companies sent emails impersonating the hosting company and asking the users to log in to an account to fix an urgent problem.
More business impersonation being used in phishing attacks mean users have to be suspicious of all emails, not just those from unknown senders.
IS YOUR COMPANY ADEQUATELY PROTECTED FROM PHISHING ATTACKS?
It’s important to implement a multi-layered security strategy to defend against one of the biggest dangers to your business’s wellbeing, phishing attacks. Contact Databranch today at 716-373-4467 x 15 or [email protected] if you would like to learn more about what options are available to improve your organizations cybersecurity. Our Foundation Security Plan offers a wide variety of benefits such as increasing malware/ransomware protection, reduces phishing compromises, and helps prevent data theft/loss.
To request a free Baseline Security Assessment, click here.
Article used with permission from The Technology Press.
Read More















